Forged Pipe Fittings: A Comprehensive Guide to Threaded and Socket Weld Connections
Introduction:
Forged Pipe Fittings: A Comprehensive Guide to Threaded and Socket Weld Connections: In any industrial piping system, the selection of appropriate pipe fittings is crucial to ensure efficient and reliable operations. Among the various types of pipe fittings available, forged fittings are widely used due to their superior strength and durability. In this blog, we will delve into the world of forged pipe fittings, with a particular focus on threaded and socket weld connections. We will explore their characteristics, advantages, applications, and considerations for proper installation. Let’s dive in!

Understanding Forged Pipe Fittings:
Forged pipe fittings are manufactured through a process known as forging, wherein metal is heated and shaped using compressive force. This process enhances the mechanical properties of the fittings, making them highly resistant to extreme temperatures, pressure, and corrosion. Forged fittings are commonly made from carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, or nickel alloys, depending on the specific application requirements.
Threaded Forged Pipe Fittings:
Threaded forged pipe fittings are designed with internal threads, allowing them to be connected to pipes with matching external threads. These fittings are commonly used in low-pressure applications and are ideal for systems requiring regular disassembly and reassembly. The threaded connection provides a secure and leak-free joint, making it suitable for non-critical applications where welding is not feasible.
Advantages of Threaded Forged Pipe Fittings:
- Easy Installation: Threaded fittings can be quickly and easily installed without the need for specialized tools or welding equipment.
- Versatility: Threaded fittings can be used in a wide range of applications, including water supply, plumbing systems, and low-pressure industrial piping.
- Accessibility: In scenarios where pipes are already installed and welding is impractical, threaded fittings offer a convenient solution for making connections.

Considerations for Threaded Forged Pipe Fittings:
- Sealant Application: Proper application of sealant, such as Teflon tape or pipe dope, is essential to ensure a reliable and leak-free joint.
- Torqueing: Care should be taken not to overtighten threaded fittings, as it can damage the threads and result in leaks. Following manufacturer guidelines for torqueing is crucial.
- Regular Maintenance: Periodic inspection and reapplication of sealant may be necessary to maintain the integrity of the threaded connections over time.
Socket Weld Forged Pipe Fittings:
Socket weld forged pipe fittings are designed with a socket-like recess that allows pipes to be inserted for welding. These fittings provide a robust and permanent joint, making them suitable for high-pressure and critical applications. Socket weld connections are particularly favored in industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and power generation.
Advantages of Socket Weld Forged Pipe Fittings:
- Strength and Reliability: Socket weld connections provide excellent strength and integrity, ensuring leak-free performance even under high-pressure conditions.
- Vibration Resistance: The welding process used in socket weld fittings enhances their resistance to vibration and mechanical stresses, making them ideal for dynamic systems.
- Clean Appearance: Socket weld connections offer a smooth and clean appearance, which is advantageous in industries where hygiene and aesthetics are crucial.
Considerations for Socket Weld Forged Pipe Fittings:
- Welding Expertise: Proper welding techniques are crucial for socket weld connections. It is essential to follow industry standards and engage qualified welders to ensure a strong and reliable joint.
- Pipe Preparation: Accurate pipe preparation, including beveling and cleaning, is vital for achieving a high-quality socket weld joint. Improper preparation can lead to weak connections and premature failures.
- Expansion and Contraction: Consideration should be given to thermal expansion and contraction when using socket weld fittings. Adequate flexibility or expansion joints should be incorporated into the system to avoid stress on the welded joints.
Size, Pressure Ratings, and Dimensions of Forged Pipe Fittings:
Forged pipe fittings are available in a wide range of sizes, pressure ratings, and dimensions to accommodate various piping system requirements. The sizes of forged fittings typically range from 1/8 inch to 4 inches, with larger sizes also available for specialized applications. The pressure ratings of forged fittings vary depending on the material, design, and temperature conditions, with common pressure classes including 2000, 3000, 6000, and 9000 pounds per square inch (psi).
The dimensions of forged fittings conform to industry standards, such as ASME B16.11 for socket weld fittings and ASME B1.20.1 for threaded fittings. These standards define the dimensions, tolerances, and threading requirements for forged pipe fittings, ensuring compatibility and interchangeability between different manufacturers.

Popular Forms and Grades of Forged Pipe Fittings in the Oil and Gas Industry:
The oil and gas industry is one of the primary sectors that extensively utilize forged pipe fittings due to its demanding operating conditions. Here are some popular forms and grades of forged pipe fittings commonly employed in the oil and gas industry:
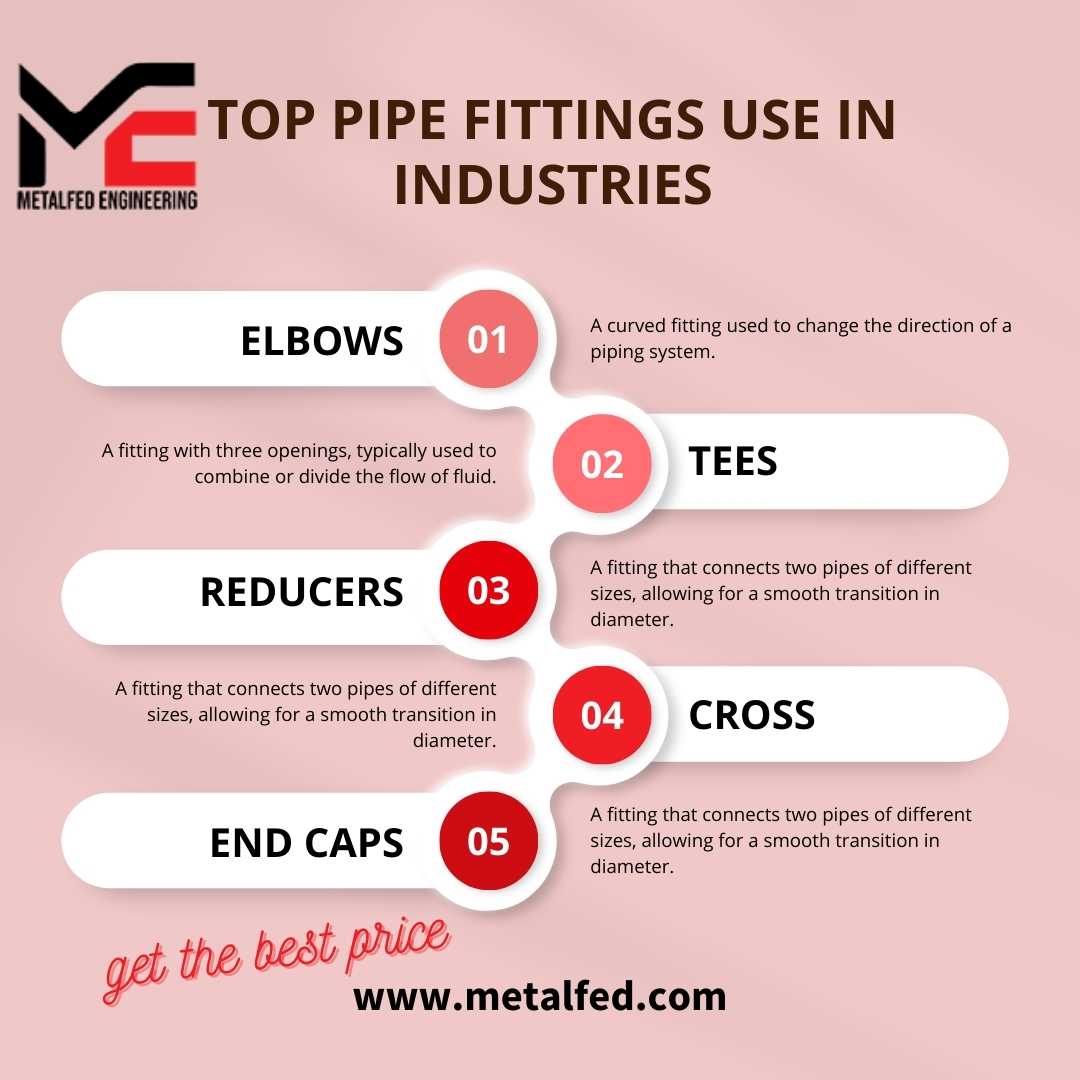
- Elbows: Elbows are fittings with a 90-degree or 45-degree bend, allowing changes in flow direction. They are widely used in oil and gas pipelines to redirect the flow around obstacles or change the pipeline’s direction.
- Tees: Tees have a T-shaped design, with one inlet and two outlets at 90-degree angles. They are utilized for branching and connecting pipelines, allowing the flow to be distributed in different directions.
- Couplings: Couplings are used to connect two pipes of the same diameter, ensuring a secure and leak-free joint. They are frequently employed in oil and gas systems for easy assembly and disassembly during maintenance or repairs.
- Caps: Caps are fittings that provide closure to the ends of pipes. They are commonly utilized in oil and gas pipelines to protect the internal contents from contamination and ensure safety during transportation or storage.
- Crosses: Crosses have a plus-shaped design, featuring four openings at 90-degree angles. They are used in complex oil and gas piping systems to connect multiple pipes at different directions, facilitating the flow distribution.
In terms of grades, the oil and gas industry often employs forged fittings made from high-performance materials to withstand harsh environments and corrosive media. Some commonly used grades include:
- Carbon Steel: ASTM A105/A105N is a commonly used grade of carbon steel forged fittings in the oil and gas industry. It offers excellent strength, impact resistance, and compatibility with a wide range of fluids.
- Stainless Steel: Grades such as ASTM A182 F304, F316, and F321 are widely used in oil and gas applications due to their superior corrosion resistance, high-temperature strength, and durability.
- Alloy Steel: Forged fittings made from alloy steels, such as ASTM A182 F5, F9, F11, and F22, offer enhanced mechanical properties and resistance to high temperatures, making them suitable for challenging oil and gas environments.
- Nickel Alloys: Nickel alloys like Inconel, Hastelloy, and Monel are utilized in extreme conditions where resistance to corrosion, high temperatures, and aggressive chemicals is paramount. These alloys are often chosen for specialized oil and gas applications such as offshore platforms and refineries.
Conclusion:
Forged pipe fittings, whether threaded or socket weld, offer exceptional strength, durability, and reliability in industrial piping systems. The choice between threaded and socket weld fittings depends on factors such as pressure requirements, installation convenience, and system dynamics. Understanding the advantages, considerations, and proper installation techniques for each type of fitting is crucial for achieving optimal performance and longevity. By selecting the right forged pipe fittings and adhering to industry best practices, you can ensure the integrity and efficiency of your piping systems.
Forged pipe fittings come in various sizes, pressure ratings, and dimensions to meet the requirements of different piping systems. In the oil and gas industry, popular forms of forged fittings, including elbows, tees, couplings, caps, and crosses, play crucial roles in ensuring efficient flow distribution and system integrity. Grades such as carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, and nickel alloys are commonly employed in the oil and gas sector due to their respective strengths, corrosion resistance, and compatibility with demanding operating conditions. By selecting the appropriate size, pressure rating, and grade of forged pipe fittings, oil and gas companies can maintain the safety, reliability, and efficiency of their piping systems.

 Venezuela
Venezuela Myanmar
Myanmar Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Belgium
Belgium Czechia
Czechia Greece
Greece Mexico
Mexico Tobago
Tobago Brazil
Brazil Chile
Chile France
France Colombia
Colombia South Africa
South Africa Jordan
Jordan Spain
Spain Hong Kong
Hong Kong Netherlands
Netherlands Poland
Poland Bangladesh
Bangladesh Indonesia
Indonesia Taiwan
Taiwan Nigeria
Nigeria Iraq
Iraq Ukraine
Ukraine Romania
Romania Cyprus
Cyprus Angola
Angola Norway
Norway USA
USA Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia Kuwait
Kuwait Thailand
Thailand South Korea
South Korea Singapore
Singapore Malaysia
Malaysia UAE
UAE Germany
Germany Italy
Italy Costa Rica
Costa Rica Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan Philippines
Philippines China
China UK
UK India
India Japan
Japan Russia
Russia Canada
Canada Iran
Iran Turkey
Turkey Morocco
Morocco Egypt
Egypt Vietnam
Vietnam Oman
Oman Australia
Australia Qatar
Qatar Portugal
Portugal